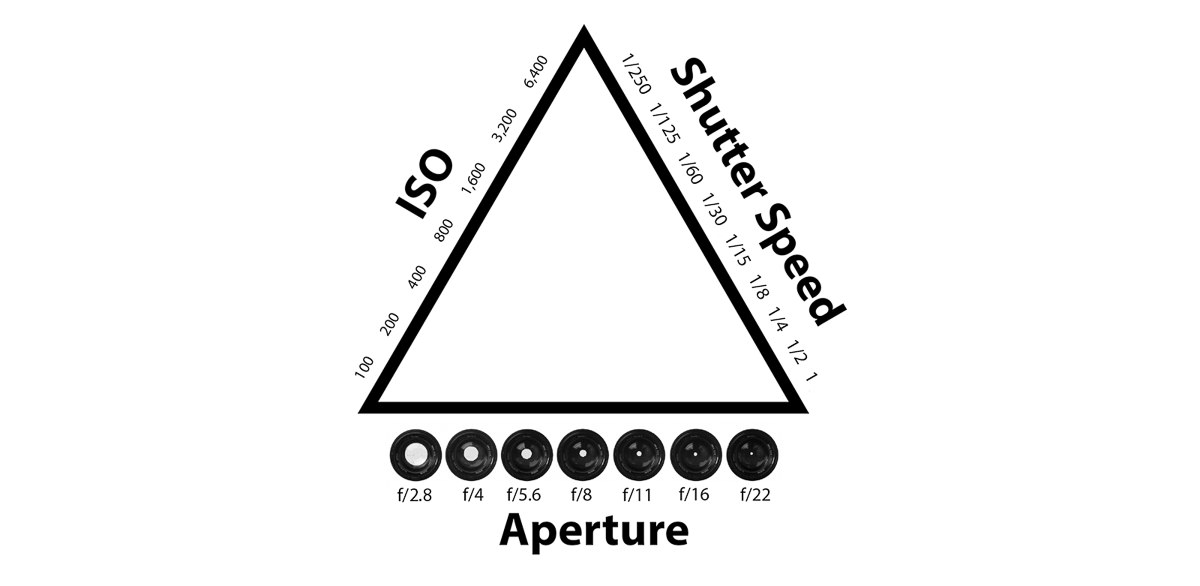
Video editing is the process of arranging media into a linear form in order to communicate a message. I found it interesting to learn that video footage used to be edited by hand using a hand device, in which the film was cut into sections with a razor blade tool and then spliced together using clear tape! I never knew this before. Machine-to-machine editing was also an intriguing topic to learn. It involved a playback deck, a source monitor, a record deck, a program monitor, and en edit controller.
Videos are edited electronically, as are film, using software programs such as Final Cut Pro, Avid Media Composer, or Adobe Premiere Pro, according to the chapter. During the production phase raw footage can be filmed and a written script can be planned before hand for films, newscasts, commercials, or other videos. A teleprompter can be used to feed words to the person that is talking on camera, so that they don’t forget what they are supposed to say or mess up in front of a live audience. This is another instance when it is important to PLAN PLAN PLAN beforehand, so that scripts or a teleprompter can be ready in advance. Below is an example of a video being edited in a program, as well as a teleprompter.


Sound bites are constructed by editors and can be short or longer clips of audio, according to the chapter. The clips can also be combined or divided in half if the sound bites are too long. The average length is 10 seconds and they should be kept UNDER 20 seconds so that they do not take up too much time and become distracting. B-roll on the other hand, is video footage that is used in conjunction with spoken audio. Natural sound, like the word suggests, is sound that comes along with shooting b-roll, and it can be sounds that occur in nature, such as grass being cut or birds chirping. A voiceover is a narrative that guides the audience over the visual portion of a video. Graphics or sound effects can also be added to supplement on-screen material.
Designing graphics for television can be tricky because the designer has to keep in mind the amount of time that it takes to read or view text on a screen, as well as how long the images will be on the screen, which will only be a few seconds. So, they must be easy to read, have solid colors, large font, be legible, and uncluttered. When considering continuity editing, the edits must be seamless so that they are not visible to the audience, which can ruin a scene. Cut–ins are a technique in which the viewer’s eye is drawn to a different view within a scene. This is done to make the viewer feel as if they are looking at things with their own eyes. Another technique is called cutting on action, which is when the editor matches continuous action during a scene to two sequential shots. For example, a wide angle shot of someone performing an action can be cut to a close-up shot.
Once the production has been finished, it is crucial to organize and store the footage in the proper place for ease of access. Creating a master project folder is the easiest way to contain all of the files that are with the project, and then you can also make other subfolders for the images, sound, and video. Media files are the files that are waiting to be edited, and high definition files require a lot of storage space, which may require hard drives that are able to store large amounts of data. In logging and batch capturing, the editor works with the clips that were captured and then logs them based on the scene, camera angle, location, or take number. Rendering a file is when the editing software makes new files for video after things have been placed by the editor, such as transitions, filters, or titles. Rending files can be done at the end, according to the book, or they can be rendered as the editor works.
A timeline displays all of the video clips on the editing software and they are ordered in linear regions which are called the tracks. Compositing a video is when two or more tracks are combined to form one image. The frames of the video are denoted by timecode. The example from the chapter is 01:18:54:27, which means a frame location of 1 hour, 18 minutes, 54 seconds, and 27 frames. You can also transform videos within the frame with the wire-frame, which allows you to rotate an image, change the speed, or add a filter. There are many different techniques to add clips to a timeline.
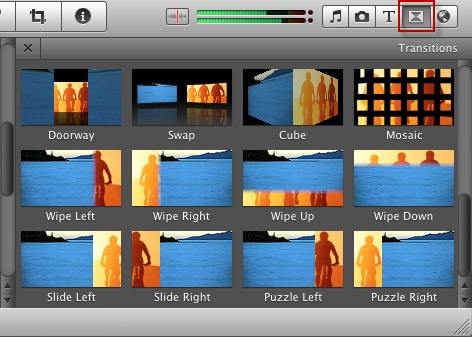
Transitions can be used to make the content flow. Cuts, fades, and dissolves are different types of transitions. A wipe is an effect that uses linear movement to transition from one image to another image, and transitions can be customized depending on the project. BUT, it is important to keep in mind the duration of the transition so that it does not take up too much of the project.
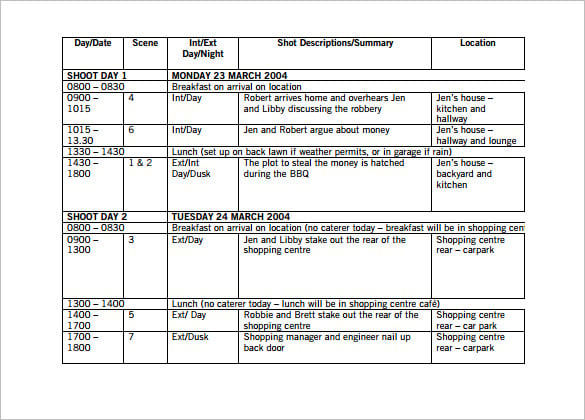
Once all of the clips are in the editing software, you can go through them in a series of passes. The first pass is when the spoken words are added, so this is when the editor would inset sound bites, voice-overs, or recorded narration. The second pass is when b-roll and natural sound can be added. Titles and graphics can be added in the third pass, sound effects and music in the fourth pass, transitions in the fifth pass, and the sixth pass would be making finishing touches. Three-point editing is also detailed within the chapter: 1. Set an IN and OUT point. 2. SET an IN point in the Timeline. 3. Perform the Edit. 4. Repeat steps 1-3 for SOT 2 and VO2. The last step is 5: Add B-roll over VO segments. Keeping in mind these steps in order is extremely helpful for editing the footage, and it is extremely important to go through every aspect with a fine-tooth comb to make sure that everything has been added correctly.
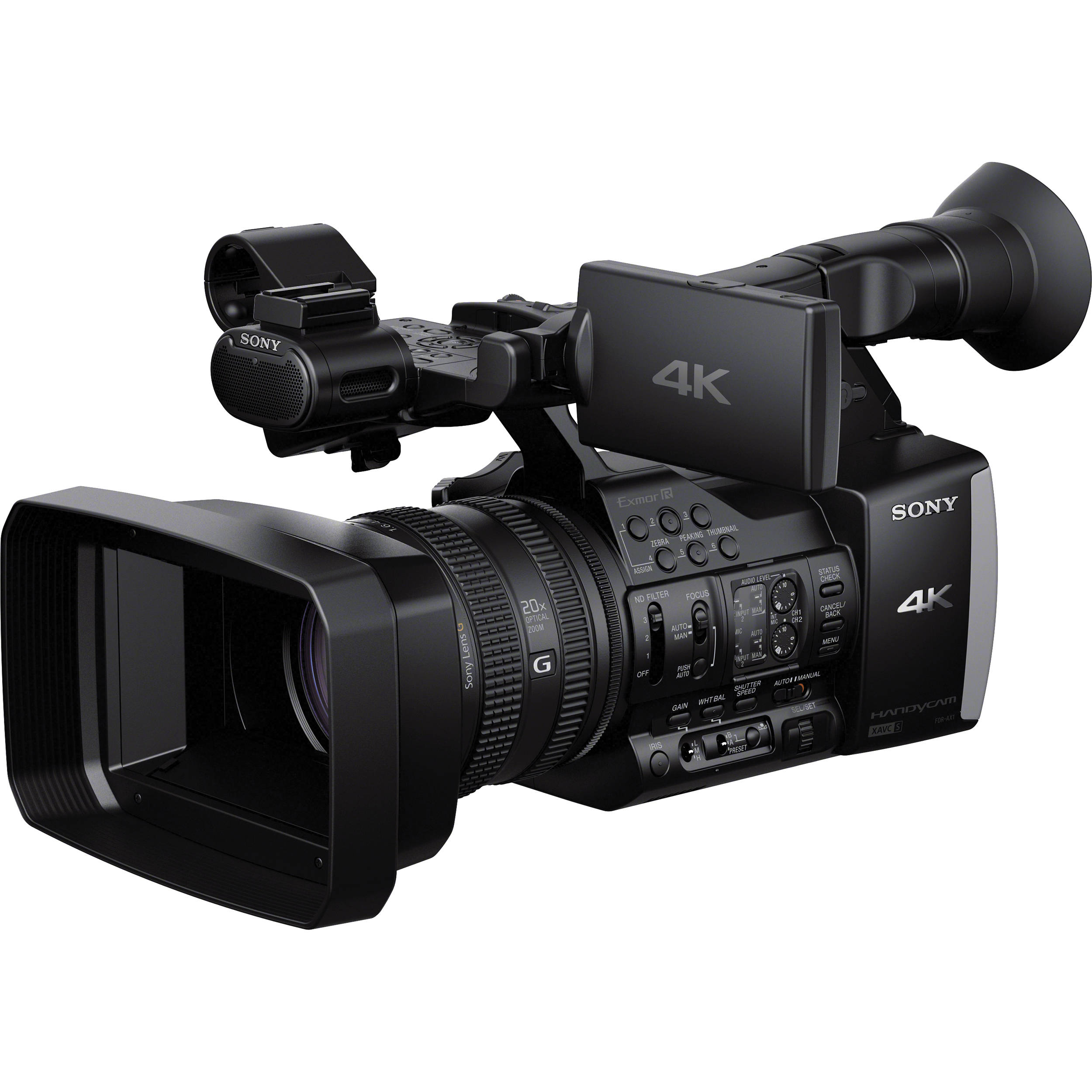











 Audio compression was enhanced through MPE-2, and MPEG-4 are recent standards that determine compression. MPEG-4 also allowed us to develop a universal format for encoding HD video on digital recorders, and for when we went to share a video online to YouTube or other video sharing websites. Plus, we also have high efficiency coding H.265, and we can use this for high definition videos. An impressive camera that was developed by Sony in the early 2000s was the XDCAM which could store up to 50GB of data. The SxS camera was developed in 2007, and now most of the Sony cameras use SxS media for recording. RED digital cameras use solid state drives to store up to 4K of recordings, and AVCHD is a format that was released by Panasonic and Sony that lets the camera user set the video quality.
Audio compression was enhanced through MPE-2, and MPEG-4 are recent standards that determine compression. MPEG-4 also allowed us to develop a universal format for encoding HD video on digital recorders, and for when we went to share a video online to YouTube or other video sharing websites. Plus, we also have high efficiency coding H.265, and we can use this for high definition videos. An impressive camera that was developed by Sony in the early 2000s was the XDCAM which could store up to 50GB of data. The SxS camera was developed in 2007, and now most of the Sony cameras use SxS media for recording. RED digital cameras use solid state drives to store up to 4K of recordings, and AVCHD is a format that was released by Panasonic and Sony that lets the camera user set the video quality.