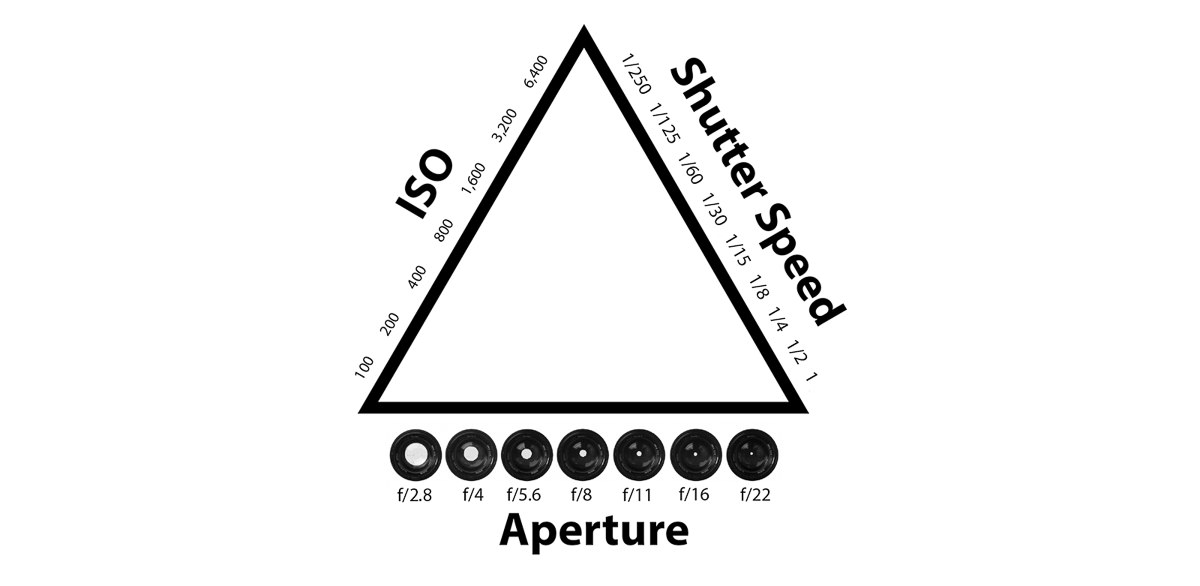
Sound can be what we hear inside or outside, in a large or small environment, or it can be what we hear from radio stations, podcasts, or songs. For sporting games that are televised on television, it is often enjoyable to be able to hear the sound of the ball dribbling on the court or the sound of a bat hitting a baseball. Sound is formally defined as a phenomenon that occurs naturally, that involves pressures and vibration. This chapter emphasizes that learning and understanding how sound works will aid in creating better sound quality for content. Sound waves are generated through energy and can travel through solids, liquids, or gases.
![]()
Amplitude is defined as the sound wave’s height, and amplitude indicates the intensity of the wave, and it is measured from the crest of the wave to the trough. It is measured in decibels that quantify the sound pressure level, which is denoted as SPL. The level that causes pain in the ear starts at 140 decibels, and repeated exposure to this level of loud sound can lead to ear damage and ultimately hearing loss. I realized while reading this 
that my music is most likely too loud in my earphones or in the car. My 16th birthday gift was extra 12-inch speakers for my car, and perhaps it is time to retire these so that I do not get hearing loss from listening to music so loud.
Frequency is a sound’s low or high pitch and people can hear frequencies starting at 20 Hz, up to 20,000 Hz. The range is divided into subgroups denoted as bass, midrange, and treble. Microphones are used to record sound waves and they convert the sound waves into electronic format. Then, the sound can be transmitted and played out loud. There are different types of microphones. Dynamic types use acoustical energy and don’t require a power source, while moving–coil microphones are attached to a coil that works with a magnet to submit current to the microphone chord. Plus, microphones can be omnidirectional, which means that there is a sphere around the microphone which picks up sound from all directions. Or, they can be bidirectional, which means that the sound is picked up equally from the front and the back.
![]()
The common microphone styles, according to the chapter, are handheld, lavalier, shotgun, and boundary. Lavalier microphones are designed to be used with no hands. It is also important to place the microphone in the right place to capture the optimal sound quality. Handheld microphones may have a windscreen which helps to decrease unwanted noise when outside. Microphones can be built–in or external. Computers have built-in microphones, which, according to the chapter, are used for speaking or having conversations, and not for recording audio. I have worked with wireless microphones before, and these are the most common that we see performers and entertainers use on a stage.
Audio connectors are used to connect microphones and audio device. A balanced cable microphone is equipped with three wires that send information back and forth in a continuous loop. There are also adaptors, which can be used to hook cables up to incompatible connectors. It is important to learn how to manage all of the cables so as to not feel overwhelmed or trip over cables while out in public. Sound checks are also a part of this, and audio will sound professional if the proper steps are taken so that the sound quality is adjusted as necessary when conducting an interview, for example. Having a good set of headphones is important as well so that capturing audio is done without making mistakes and errors. From this chapter, I learned that having the proper equipment throughout every stage and knowing how to use it is key to having successful audio production!





 Audio compression was enhanced through MPE-2, and MPEG-4 are recent standards that determine compression. MPEG-4 also allowed us to develop a universal format for encoding HD video on digital recorders, and for when we went to share a video online to YouTube or other video sharing websites. Plus, we also have high efficiency coding H.265, and we can use this for high definition videos. An impressive camera that was developed by Sony in the early 2000s was the XDCAM which could store up to 50GB of data. The SxS camera was developed in 2007, and now most of the Sony cameras use SxS media for recording. RED digital cameras use solid state drives to store up to 4K of recordings, and AVCHD is a format that was released by Panasonic and Sony that lets the camera user set the video quality.
Audio compression was enhanced through MPE-2, and MPEG-4 are recent standards that determine compression. MPEG-4 also allowed us to develop a universal format for encoding HD video on digital recorders, and for when we went to share a video online to YouTube or other video sharing websites. Plus, we also have high efficiency coding H.265, and we can use this for high definition videos. An impressive camera that was developed by Sony in the early 2000s was the XDCAM which could store up to 50GB of data. The SxS camera was developed in 2007, and now most of the Sony cameras use SxS media for recording. RED digital cameras use solid state drives to store up to 4K of recordings, and AVCHD is a format that was released by Panasonic and Sony that lets the camera user set the video quality.